Power Transformer
Power Transformer is a building intended to separate two circuits to protect against overload damage or to force power into another circuit. It works as a buffer between circuits, providing up to 1000 W from its internal battery to one circuit while consuming power from the other circuit. Since the output is limited, it can safely convert power from a higher wattage source (e.g. Heavi-Watt Wire, which can carry up to 20 kW) down to a lower wattage (e.g. Wire, which can only carry up to 1 kW). Multiple transformers can be connected on a circuit as either consumer or producer.
Usage
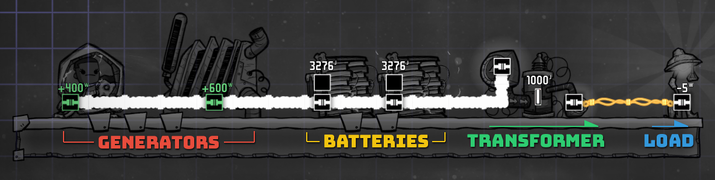
Transformers have an input side (the upper attachment point) and an output side (the lower attachment point). Typically, high-power circuits should enter the transformer through its upper input, and will output up to 1 kW on the output side.
Typically, generators and Batteries will be attached on a Heavi-Watt Wire grid, giving them a 20 kW capacity (allowing up to 33 Coal Generators). Multiple transformers can then be attached to supply power consumers attached to a lower wattage cable able to cross tiles.
In this scenario, batteries on the output side of the transformers would be avoided, as batteries have no limit to output rate. A transformer can resist damage when power draw crosses above 1 kW, but a battery can cross that limit and overload a circuit.
Alternatively, transformers can be used to draw power from a low wattage circuit attached to multiple power producers and output into a higher wattage circuit. This would protect the lower circuit from overload while still providing to the main power circuit and benefitting from the advantages of using low wattage cables.
Notes
- Transformers will operate without any power cost or charge loss unless disabled by automation or disconnected from an output circuit. In which case, the internal battery will rapidly drain.
- Automation can be used to interrupt power flow in the same way as Switches and Power Shutoffs. However, this will cause power runoff.
- Two transformers drawing from a high wattage input can be paired to fully provide for a Conductive Wire grid safe from overloading.
- A power transformer will produce heat as long as it contains some energy, irrespective of the power input/output.
- The internal battery is limited to a recharge rate of 1 kW (or 200 J per game tick) and acts as a regular battery.
- On its own, the battery of a transformer will limit the available power to 1 kW and prevent overload. However, if more batteries or transformers are connected, the increased available power may cause overload damage to happen.
History
- EU-279457: Introduced.
- QLM1-299745: Renamed from Small Power Transformer.
- U51-594767: Potential Load tooltip should now consider Power Transformer consumption.